Dive into our comprehensive radiology MCQ post featuring 10 (21-30) carefully selected questions, each illustrated with high-quality images. Understand the reasoning behind each answer with our detailed explanations, helping you grasp the concepts thoroughly. Whether you’re a student gearing up for exams or a professional looking to refresh your skills, this guide is designed to boost your radiology expertise.
Find Radiology MCQS 11-20 Here
Radiology MCQS 21-30
21. As a result of the tetralogy of Fallot, the overall heart size is
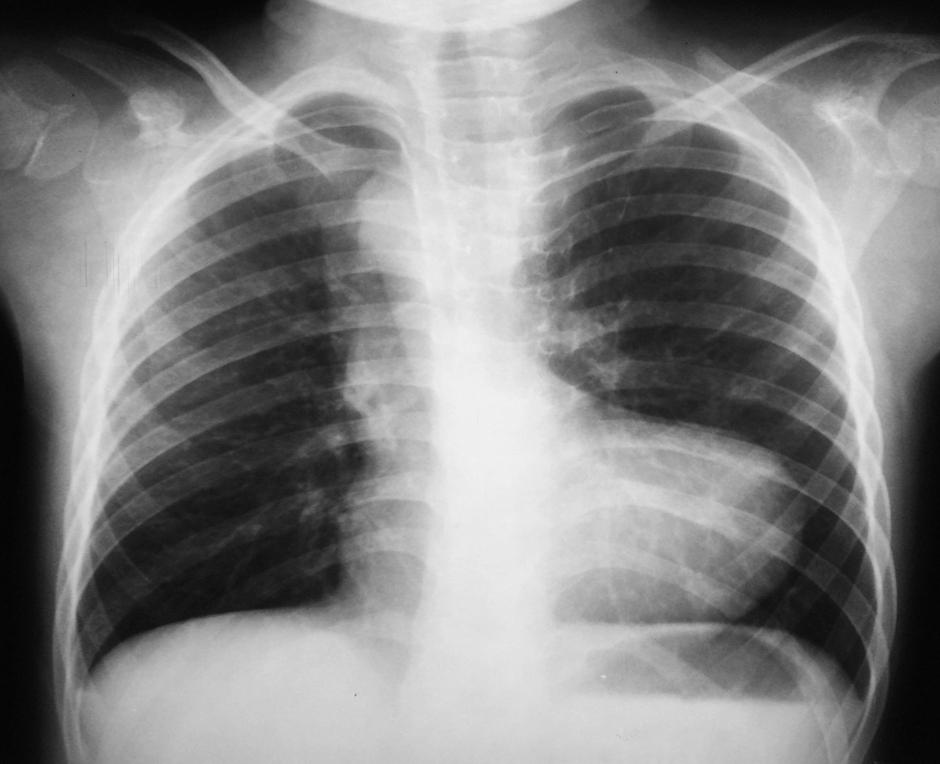
A. Markedly enlarged.
B. Normal or relatively small
C. Slightly enlarged.
D. Moderately enlarged.
E. Neutral Size
Answer: B
There is no evidence that cyanosis or a right-sided aortic arch are associated with tetralogy of Fallot, but there is evidence that cardiomegaly is present and there is an increase in pulmonary vascularity. (Answer A is incorrect). Aortas are positioned incorrectly in the tetralogy of Fallot. The ventricular septal defect is directly above the hole in the heart wall. This results in a mixture of oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood being delivered to the aorta from both of ventricles. (Answer B is correct). Several conditions can cause an enlarged heart (cardiomegaly), including damage to the heart muscle or conditions that force the heart to pump harder than normal (Answers C, D, and E are incorrect).
22. Aortic calcification can be diagnosed using fluoroscopy by seeing.

A. Side-to-side movement
B. Up and down movement
C. Combined movement.
D. Down movement
E. None
Answer: A
Cardiac fluoroscopy is a highly specific test that can be performed easily, inexpensively, and noninvasively, and is applicable to large populations of patients. (Answer A is correct). The process of obtaining images rapidly and displaying them in real-time on a screen. (Answers B, C, and D are incorrect). Using X-ray images, fluoroscopy tracks the motion of bones and other biological tissue. Answer E is incorrect).
23. A variety of factors contribute to pericardial calcification except
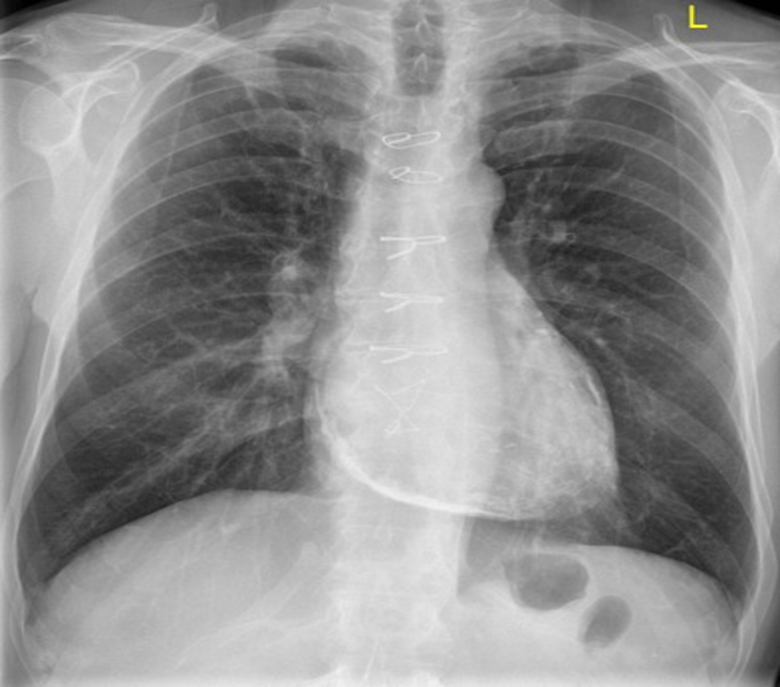
A. Radiotherapy to the mediastinum
B. Methysergid therapy
C. Anticoagulant therapy
D. Benign pericarditisis
E. Dermatomyositis
Answer: E
Radiation-induced valvular heart disease increases the risk of valvular heart disease after mediastial radiation therapy.(Answer A is incorrect). Based on our findings, methysergide induces selective vasoconstriction in the external carotid circulation under our experimental conditions without affecting heart rate or blood pressure. (Anwser B is incorrect). The purpose of anticoagulants is to prevent blood clots. The purpose of these drugs is to reduce the risk of developing serious conditions such as strokes and heart attacks in people who are at high risk of clots. (Answer C is incorrect). High fever and chest pain are common symptoms of pericarditis. Usually, it doesn’t cause any serious health issues, but it can be dangerous. Consult a doctor if you are experiencing chest pain. (Answer D is incorrect) . Skin rash and muscle weakness are the symptoms of Dermatomyositis, a rare disease. Red or purple rashes appear on the skin and eyelids, calcium deposits are present under the skin, muscles are weak, and there is difficulty swallowing or talking. (Answer E is correct).
24. Angiocardiography is best suited to observing the mitral valve in this position.
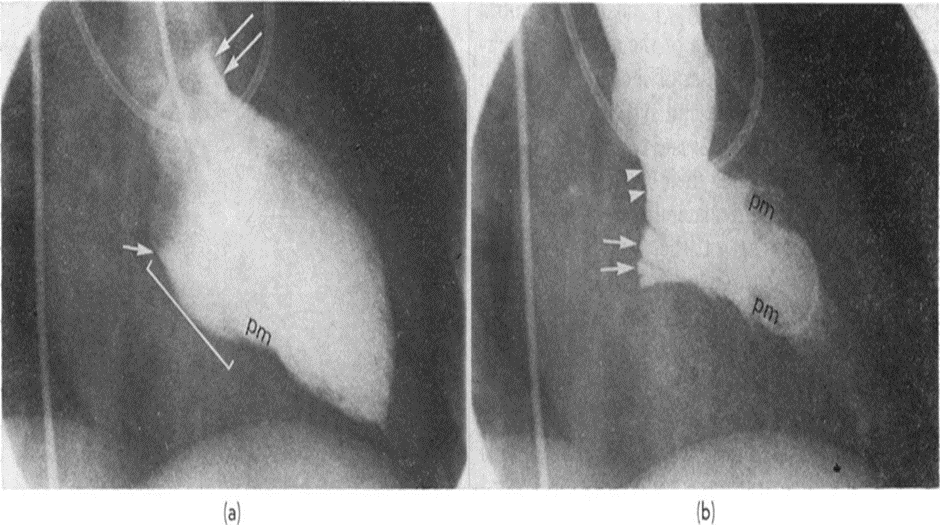
A. Frontal view
B. Lateral view
C. Right anterior oblique view
D. Left anterior oblique view.
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Blood vessels in the heart can be blocked or narrowed by a coronary angiogram. Cardiovascular angiograms use X-ray imaging to view the blood vessels in your heart. (Answer A is incorrect). It is uncommon to use the lateral view, which requires positioning the hands above the head so that the patient’s arms are not overlapping. In the case of distal LAD fields of interest, this requirement is not applicable. (Answer B is incorrect). This view of the RAO shows the conus branch and sinus node artery pointing in opposite directions. (Answer C is correct). Typical LAO views show the full length of the right coronary artery in the shape of a C. The crux cordis is the point at which the right coronary artery divides into PDA and PLV. At the posterior end of the atrioventricular groove, the crux cordis connects to the interventricular groove. (Answers D and E are incorrect)
25. Small intestinal malabsorption syndrome is characterized by all the X-ray findings except one:
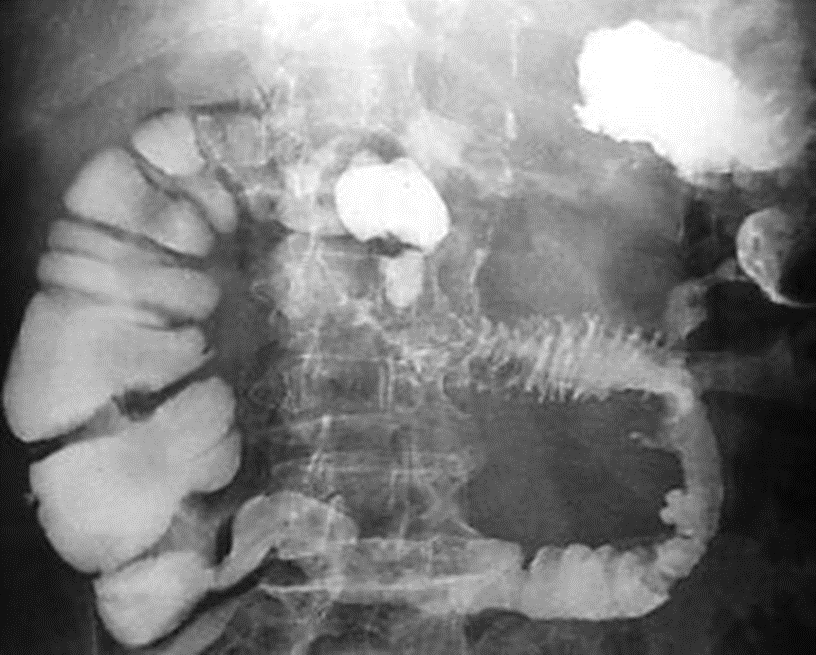
A. Increased transit time.
B. Mucosal atrophy
C. Dilatation of the bowel
D. Fluocculation of barium
E. Decreases transit time
Answer: A
Transit time for the bowels varies, even for a single person. It takes 30 to 40 hours for someone who is not constipated to transit through the colon. A normal period is 72 hours, up to a maximum. (Answer A is correct). In addition to decreased intestinal function, mucosal atrophy is characterized by morphological changes, such as decreased villous height, crypt depth, surface area, and several epithelial cells.(Answer B is incorrect). An obstruction or ileus is indicated by a dilated small bowel larger than 3 cm. It is indicative of an obstruction or other intestinal inflammatory cause when the bowel wall is edematous beyond 3 mm. (Answer C is incorrect). As part of a fluoroscopic examination, flocculation occurs when a barium suspension breaks down. A barium suspension eventually separates out in the small bowel environment, which can happen between 15 minutes and three hours into a barium study. (Answer D is incorrect). In most cases, small-bowel transit is considered delayed when there is no activity or limited activity in the terminal ileum reservoir after 6 h.(Answer E is incorrect).
26. A mediastinal shadow does not form on the right side by

A. SVC
B. Right innominate
C. RA
D. RV
E. APV
Answer: D
In the mediastinum, there is only one systemic vein that is larger than the superior vena cava: the superior vena cava (SVC). Various imaging techniques (such as radiography, computed tomography [CT], magnetic resonance venography [MR]), and conventional venography, can be used to identify congenital tumors and pathological conditions that affect the SVC. (Answer A is incorrect). An important vascular structure was seen on the CT images arising from the junction of the right and left innominate veins (Answers B and C are incorrect). Chest manifestations of paraneoplastic syndromes can occur with anterior mediastinal masses, especially thymomas. There is a strong correlation between ptosis, dysphagia, weakness, and fatigue, which are all symptoms of myasthenia gravis, the most common paraneoplastic syndrome associated with ptosis. (Answer E is incorrect).
27. To diagnose suspected uric acid calculi, the best imaging method is:

A. Plain film of the abdomen
B. Ultrasonography
C. Intravenous pyelography
D. Radionuclides
E. Fluoroscopy
Answer: C
X-rays of the abdominal cavity are common diagnostic tools that produce images of the stomach, liver, intestines, and spleen, among other organs.(Answer A is incorrect).In addition to checking for thyroid growths, breasts, testes, and limbs, ultrasound imaging is also useful for checking some lymph nodes within the body. (Answer B is incorrect). Intravenous pyelography consists of x-raying the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and prostate in men while injecting a contrast dye. (Answer C is correct). A fluoroscopy is a medical procedure in which x-rays are passed through the body slowly over time to make a real-time video of body movements. (Answer E incorrect).
Read USMLE Preparation Guide Here
28. An X-ray of a child’s skull shows signs of increased intracranial tension

A. Separation of the sutures
B. Tens anterior fantanelle
C. Silver-beaten appearance of the bones.
D. Tens posteriot fantanelle
E. All the above
Answer: E
Various conditions or diseases can cause the sutures to spread apart because of abnormally high pressure within the head. There could be pressure within the skull resulting in separated sutures. (Answer A is incorrect). A tense or bulging fontanelle is caused by a build-up of fluid or swelling of the brain, which increases pressure inside the skull. (Answer B is incorrect). Multiple skull bones exhibit prominent convolutional marks that are commonly referred to as ‘silver beaten’ skulls. In addition to craniosynostosis and obstructive hydrocephalus, intracranial masses are believed to be the underlying causes. (Answer C is incorrect). It is important to measure the size of the anterior and posterior fontanels, as well as the shape, circumference, and suture ridges of a newborn’s skull. (Answer D is incorrect). Regarding increased intracranial pressure in children’s skulls, all factors are true. (Answer E is correct).
29. The most useful application of echoencephalography is to detect.

A. Ventricular dilatation
B. Midline shift
C. Epilepsy
D. Vascular lesions
E. Carcinomas
Answer: A
In failing hearts, ventricular dilation is the first compensatory response that restores stroke volume. (Answer A is correct). The midline shift is determined by the degree of horizontal shift of the midline cerebral structures as observed on axial images. (Answer B is incorrect). Epilepsy is a common condition that causes frequent seizures in the brain. (Answer C is incorrect). In addition to birthmarks, vascular lesions commonly occur in the skin and underlying tissues. (Answer D is incorrect). Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, if left untreated, can damage healthy tissue nearby, spread to the lymph nodes or other organs, and may even be fatal. (Answer E is incorrect).
30. In Target Signs, “Sonographically” means.
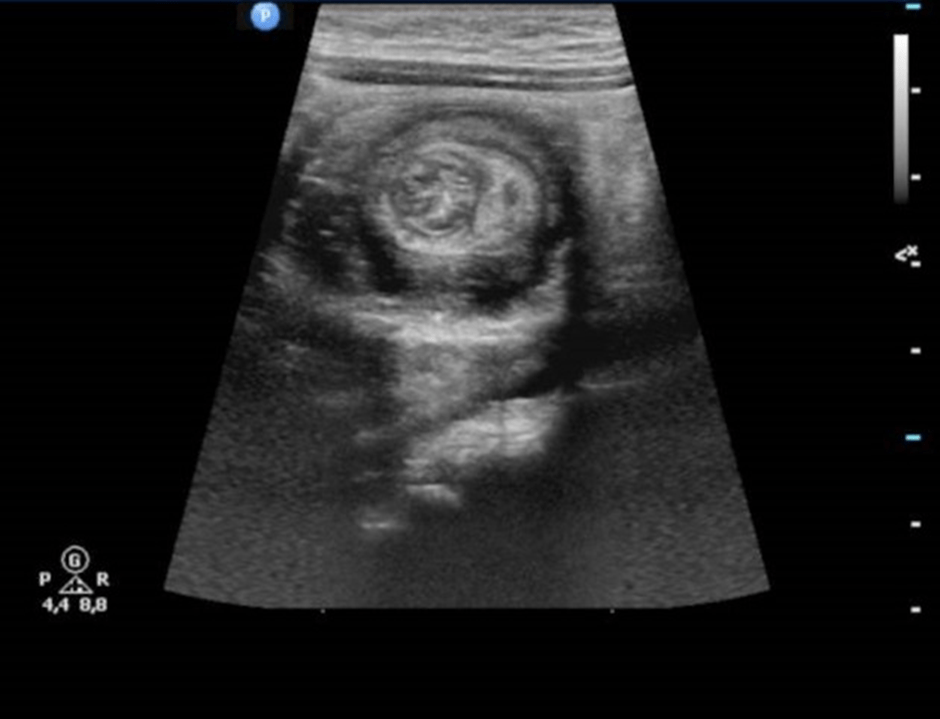
A. Ovarian carcinoma
B. Ectopic kidney
C. Intussusception
D. Liver metastasis
E. Acute cholecystitis
Answer: C
A carcinoma is an epithelial tumour that is cancerous. Malignant ovarian cancers are predominantly epithelial. Different types of epithelial ovarian carcinoma can be classified based on several features of these tumour cells (in the lab). (Answer A is incorrect). There are three types of ectopic kidneys: those located below, above, or on the opposite side of the urinary tract from their normal position. (Answer B is incorrect). When an intussusception is present, it may be evident on an ultrasound, X-ray, or computerized tomography (CT) scan. The intestine coiled within the intestine typically appears as a “bull’s-eye” on imaging. (Answer C is correct). Metastases to the liver result from cancer spreading from another part of the body. (Answer D is incorrect). In acute cholecystitis, the gallbladder swells (inflammation). It is a potentially serious condition that usually needs to be treated in a hospital. (Answer E is incorrect).


