Preparing for the USMLE? Our curated set of radiology MCQs is designed to help you succeed. Each question is crafted to reflect the style and difficulty of the actual exam, covering key topics and common pitfalls. Whether you’re brushing up on basics or seeking to solidify your expertise, these MCQs will aid in your revision and boost your confidence. For more in-depth study, refer to this article on Radiology from Medscape and explore the USMLE Preparation Resources. Dive in and start preparing for success today!
USMLE Preparation Radiology MCQS 31-40
Find Radiology Mcqs 21-30 Here
1. Osteosclerotic bone secondary lesions occur in
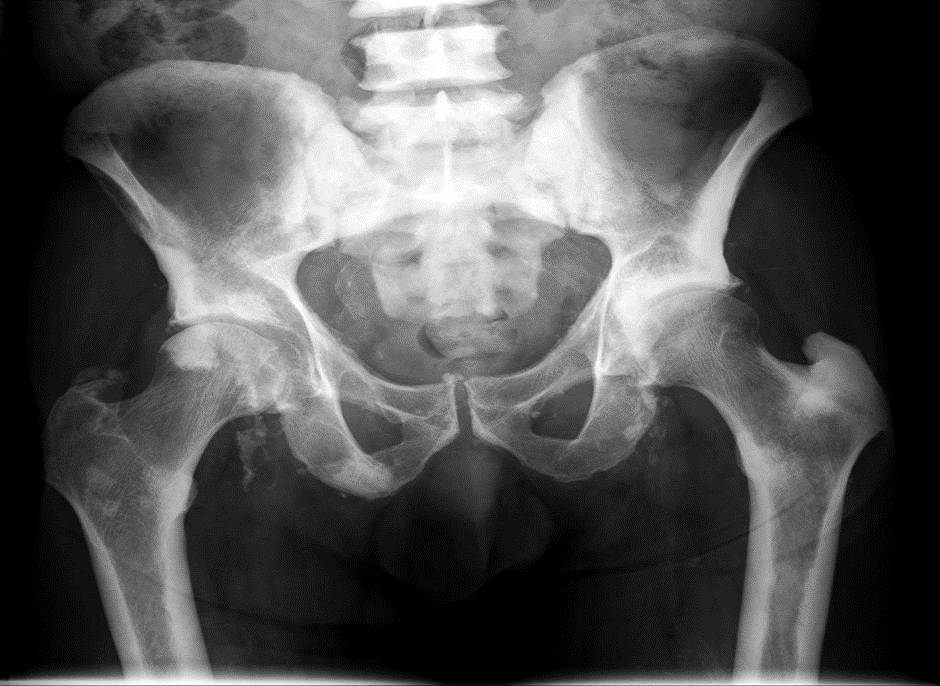
A. Carcinoma thyroid
B. Carcinoma prostate
C. Carcinoma stomach
D. Carcinoma lung
E. Ovarian carcinoma
Answer: B
Radiation exposure is the most common cause of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC), which is the most common form of well-differentiated thyroid cancer. (Answer A is incorrect). In addition to the prostate, prostate cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body as well. The lymph nodes and bones are the most common sites where prostate cancer metastasizes. (Answer B is correct). Those cells that produce mucus are responsible for causing adenocarcinoma stomach cancer. There are several types of stomach cancer, but this is the most common. (Answer C is incorrect). Cancer-related deaths related to lung cancer are among the highest in the world. Approximately 85% of cases are caused by smoking cigarettes. The most common symptoms are coughing, chest discomfort, weight loss, and haemoptysis. (Answer D is incorrect). Most ovarian cancers that are caused by tumours of the germ cells or the stroma survive. Most ovarian cancers, however, are epithelial carcinomas, which have a lower survival rate. (Answer E is incorrect).
2. What is the finding of this image?
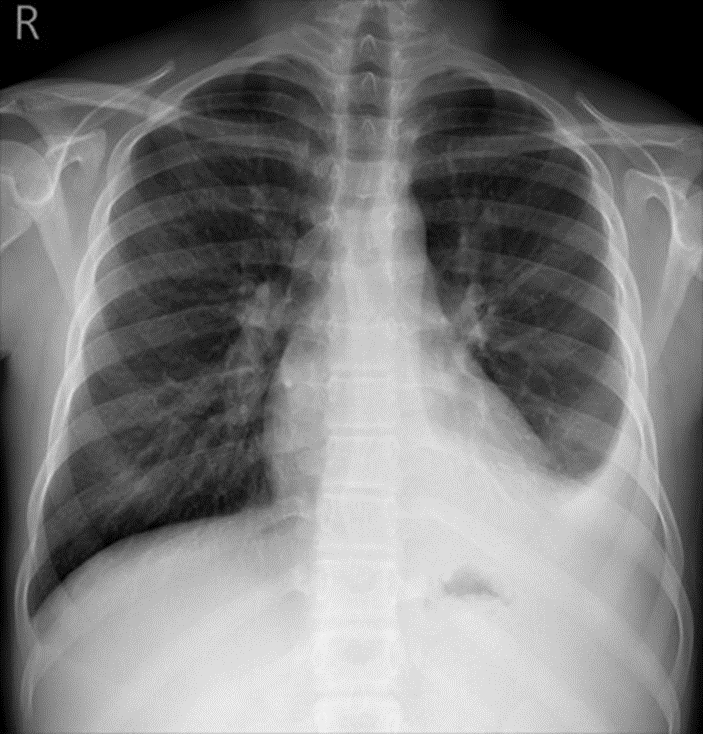
A. Normal X-ray image
B. Sail sign
C. Meniscus sign
D. Pneumothorax
E. Air bronchogram
Answer: C
An X-ray shows dark air, so a clear and healthy lung should appear dark as well: not quite black, since there is still tissue there, but still dark. (Answer A is incorrect). Known as the anterior fat pad sign, the sail sign on an elbow radiograph depicts the elevated anterior fat pad creating a silhouette similar to a billowing spinnaker sail from a boat. (Answer B is incorrect). In hydatid disease, a crescent-shaped collection of air covers a rounded lung mass, but the feature can also occur in benign conditions. (Answer C is correct). Pneumothoraxes are caused by the leakage of air between the chest wall and the lung. Your lung collapses due to the force of air pushing on it. (Answer D is incorrect). Rare exceptions apply to the diagnosis of alveolar disease using the air bronchogram sign. (Answer E is incorrect).
3. On the left lung detail image, what finding can be seen?

A. Mesothelioma
B. Asbestosis
C. Pleural effusion
D. Calcified pleural plaques.
E. Normal X-ray image
Answer: D
Several organs in the body have a lining that covers them on the outside, which is called mesothelioma. (Answer A is incorrect). The disease asbestosis is caused by the inhalation of asbestos fibers. It is possible to suffer from lung tissue scarring and shortness of breath after prolonged exposure to these fibers. (Answer B is incorrect). The presence of fluid around the lung may appear less serious than it actually is. (Answer C is incorrect). The lungs can be seen with translucent white deposits called calcified pleural plaques. When asbestos exposure is present, plaques may be asymptomatic. (Answer D is correct). When the lungs are clear and healthy, they should appear dark on an X-ray: not quite black, since there is still tissue, but still quite dark. (Answer E is incorrect).
4. 20-year-old female is coughing and has a high temperature. How would you describe the appearance?
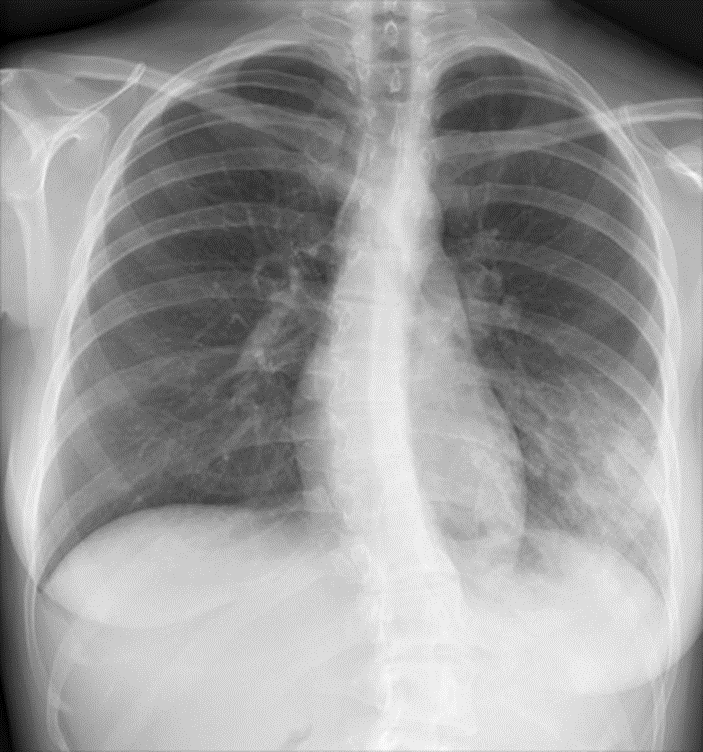
A. Normal Image
B. Inadequate due to patient rotation
C. Pleural effusion
D. Lung cancer
E. consolidation
Answer: E
When the lungs are healthy. The lungs of a healthy person look and feel like sponges. With every breath, they squish and expand, giving them a pink color. Their main function is to take oxygen from the air and transport it to your blood. (Answer A is incorrect). By measuring the distance between the clavicles’ medial edges and the vertebral spinous processes, rotation can be assessed.(Answer B is incorrect).This fluid collects abnormally, and excessively in the pleura. (Answer C is incorrect). Cancer of the lungs could spread to other organs, such as the brain, or to lymph nodes. There is also a possibility that cancer may spread from another organ to the lungs. (Answer D is incorrect). In lung consolidation, the margins of vessels and airways are obscured by a homogeneous increase in lung parenchymal attenuation.(Answer E is correct).
Checkout these Useful External Resources for usmle preperation
An authoritative resource on radiology fundamentals. Check it out here.
USMLE Official Site: Access practice materials and exam preparation guidelines. Visit the site here.
5. What is the present finding in this x-ray?
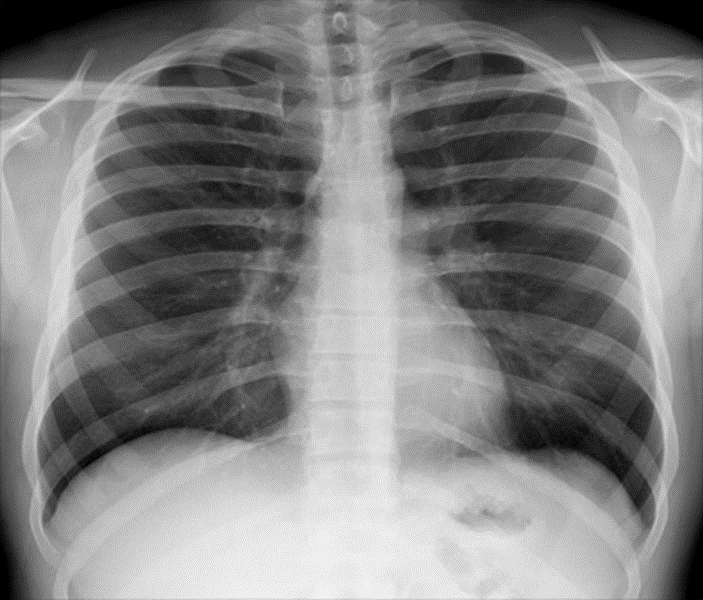
A. Normal chest X-ray
B. Cardiomegaly
C. Pectus excavatum
D. Azygos fissure
E. Free gas under the diaphragm
Answer: A
An X-ray shows air as dark, so when the lungs are clear and healthy, they ought to appear dark, not quite black, because there is still some tissue. (Answer A is correct). Heart disease, one of the most common causes of cardiomegaly, affects many people. According to estimates, 18 million Americans over 20 are affected by the disease. (Answer B is incorrect). People with pectus excavatum have their breastbones recessed into their chests. (Answer C is incorrect). The right posterior cardinal vein migrates abnormally through the right lung lobe instead of going over the apex during embryological development, resulting in an azygos lobe. (Answer D is incorrect). It is possible to perceive diaphragmatic muscle slips as arcuate bands of soft tissue, arching parallel to the diaphragmatic dome when there is free air under the diaphragm. (Answer E is incorrect).
6. 22 years old female got a cough, losing weight, and clubbing her fingers. Which of the following statements is true?
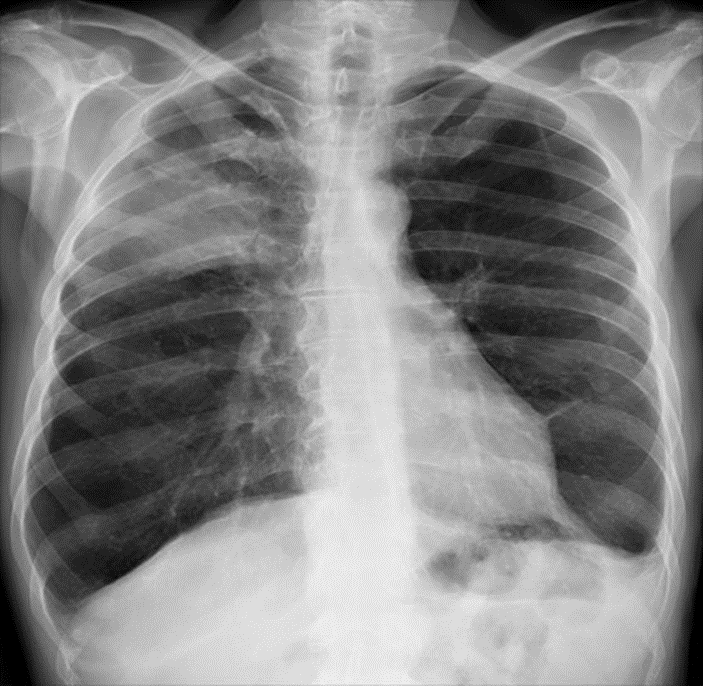
A. Lung cancer can be diagnosed by this image.
B. Pneumonia can be diagnosed based on the image.
C. Pleural effusions are responsible for the narrowing of the costophrenic angles.
D. Hyper expansion of the lungs
E. Increased heart size.
Answer: D
You may be diagnosed with an abnormal mass or nodule on an X-ray of your lungs. Small lesions in your lungs can be detected by CT scan even if they cannot be seen on X-rays. (Answer A is incorrect). Infections caused by bacteria lead to pneumonia, a disease affecting the lungs. In order to achieve successful treatment, an early diagnosis is essential. A chest X-ray can generally be used by expert radiologists to diagnose the disease. (Answer B is incorrect). The classic sign of pleural effusion is a narrowing of the costophrenic angle. Blunting can occur from scarring or chronic atelectasis, which are causes of minor blunting. (Answer C is incorrect). A person with hyperinflated lungs suffers from overinflated lungs caused by trapped air. (Answer D is correct). Any condition that increases the heart’s pumping effort (cardiomegaly) can cause an enlarged heart. (Answer E is incorrect).
7. What finding is present in this study?
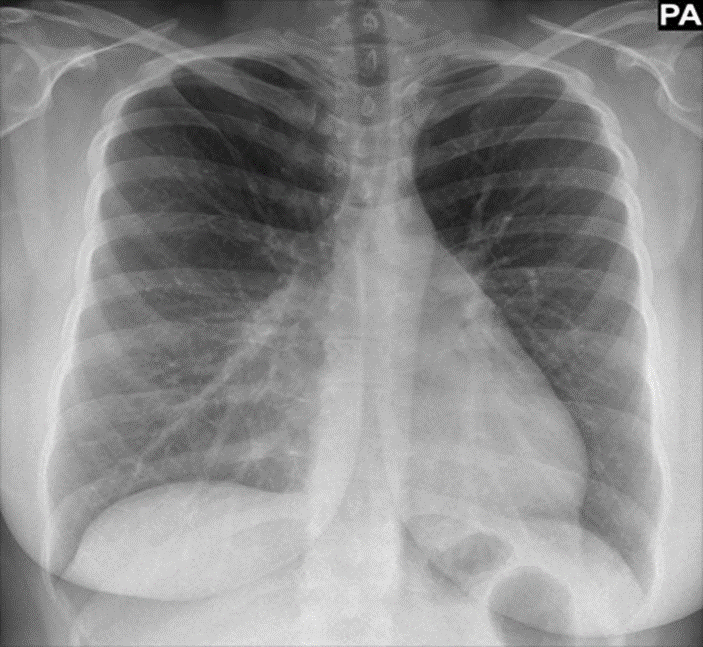
A. Normal
B. Dextrocardia
C. Pectus excavatum
D. Right middle lobe pneumonia
E. Cardiomegaly
Answer: C
You can see images of your heart, lungs, blood vessels, airways, and chest and spine bones with chest X-rays. As well as revealing fluid around your lungs, chest X-rays can also reveal air surrounding your lungs. (Answer A is incorrect). As opposed to its normal position on the left side of the chest, the heart lies on the right side in dextrocardia. (Answer B is incorrect). Breastbones that sunk deep into a person’s chest are known as pectus excavatum. (Answer C is correct). A patient with middle lobe syndrome usually presents with recurrent pneumonia-like symptoms including chronic cough, haemoptysis, and dyspnea. (Answer D is incorrect). Many times, cardiomegaly is just a temporary condition that will resolve without any further medical intervention. It is possible, however, for some people to be permanently cardiomegaly. Preventing more serious heart damage requires treating this symptom and its underlying cause. (Answer E is incorrect).
8. An X-ray of the chest close-up shows which finding?

A. Bronchiectasis
B. Septal lines (Kerley B lines)
C. Accessory fissures
D. Lung fibrosis
E. Normal chest X-ray
Answer: B
It is a long-term condition characterized by widened airways in the lungs, leading to excess mucus build-up that can make the lungs more susceptible to infection. (Answer A is incorrect). As a result of prominent interlobular septa in the pulmonary interstitium, septal lines, also known as Kerley lines, can be observed. (Answer B is correct). Common congenital variations include accessory fissures. A cleft of varying depth, lined by the visceral pleura, occurs between the bronchopulmonary segments. (Answer C is incorrect). Fibrosis of the lungs occurs when lung tissue becomes scarred and damaged. (Answer D is incorrect). The lungs should appear not quite black on an X-ray when they are healthy and clear. (Answer E is incorrect).
9. Which of these statements is true regarding this x-ray?

A. A repeat X-ray is necessary due to the poor quality of the X-ray.
B. Advancing the endotracheal tube is necessary.
C. It is recommended that the internal jugular catheter be removed.
D. Dispose of the nasogastric tube
E. Lung function is normal.
Answer: D
Anatomical and/or disease features that are not clearly visible should be repeated only if the anatomy and/or disease are not clearly visible. Patients and imaging services are both adversely affected by repeat imaging. (Answer A is incorrect). Maintaining airway patency: Preventing tracheal trauma, preventing secretion aspiration, and providing general guidelines and procedures. (Answer B is incorrect). Put sterile gauze swabs over the site of insertion and gently remove the catheter with one hand. (Answer C is incorrect). The NG tube will be removed when the output of the tube is less than 500 mL over a 24-hour period, with at least two other signs of bowel function returning. (Answer D is correct). Liters are used to measure lung volume. It is estimated that each person will have a different total lung capacity (TLC) based on their age, height, gender, sex and ethnicity. There is usually a range of 80% to 120% of the predicted result in normal cases. (Answer E is incorrect).
10. What is the most likely physical examination sign you would expect to see when this X-ray is taken?

A. Having left-sided bronchial breathing.
B. Tracheal deviation
C. The right side of the chest is hyper resonant to percussion
D. Normal examination findings
E. Finger clubbing
Answer: C
A bronchial breath sound is a loud, harsh breathing sound that has a midrange pitch. Due to their longer expiratory duration than their inspiratory duration, doctors usually associate these sounds with exhalation. (Answer A is incorrect). When abnormal pressure in your chest cavity or neck pushes your trachea to one side, it results in tracheal deviation. (Answer B is incorrect). There may be a pneumothorax on one side of the chest if there is an area of hyper resonance on that side. (Answer c is correct). It usually takes about 30 minutes to perform a physical examination from head to toe. Observation, palpitation, percussion, and auscultation are used to evaluate your body and measure your vital signs. (Answer D is incorrect). The condition of clubbed fingers occurs when there is chronically low oxygen levels in the blood, often due to diseases of the heart or lungs. (Answer E is incorrect).


